Most of the basic physics textbooks talk on the topic of horizontal range of the projectile motion. Initial velocity is the velocity at time interval t 0 and it is represented by u.
Example Calculation Of Horizontal Velocity Horizontally Launched Projectiles Youtube
The horizontal displacement of a projectile is dependent upon the horizontal component of the initial velocity.
Initial horizontal velocity formula physics. V i stands for initial velocity d stands for distance. It is the velocity at which the motion starts. As discussed in the previous part of this lesson the horizontal displacement of a projectile can be determined using the equation x v ix t.
1 if time acceleration and final velocity are provided. Horizontal velocity initial horizontal velocity. X horizontal distance m y vertical distance m v velocity combined components m s v x horizontal velocity m s v y vertical velocity m s.
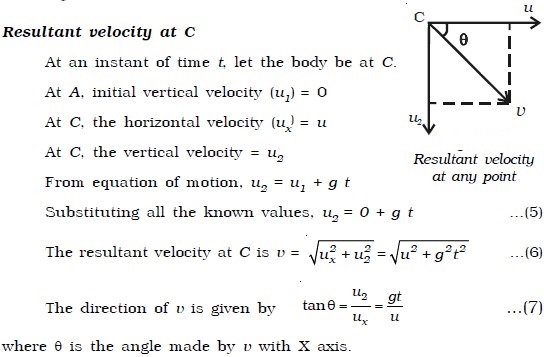
In physics the projectile motion is broken into two components. The movement of a projectile in a 2d plane can be described by analyzing the. V a times t however to write a motion equation that treats horizontal and vertical velocity separately you must distinguish the two by using v x and v y for horizontal and vertical velocity respectively.
R horizontal range m v 0 initial velocity m s g acceleration due to gravity 9 8m s 2 theta angle of the initial velocity from the horizontal plane radians or degree derivation of the horizontal range formula. Writing down all of the known information is the first step to finding the right equation. The horizontal range depends on the initial velocity v 0 the launch angle θ and the acceleration due to gravity.
The unit of horizontal range is meters m. Vertical distance from the ground is described by the formula y g t 2 where gis the gravity acceleration and his an elevation. If you know values for the distance time and acceleration you can use the following equation.
R horizontal range m v 0 initial velocity m s g acceleration due to gravity 9 80 m s 2 θ angle of the initial velocity from the horizontal plane radians or degrees. For every object the gravitational force causes a constant acceleration of 32 2 ft s 2 or 9 8 m s 2 towards the earth. In physics anybody thrown into space by a force is often referred to as a projectile.
V x v xo. V i d t a t 2 understand what each symbol stands for. For a general velocity problem you can simply write an equation using v for velocity such as.
In most of the cases of projectile motion the vertical component is due to the action of gravity. Vertical velocity initial vertical velocity acceleration due to gravity time v y v yo gt. Horizontal distance can be expressed as x v t.
They are four initial velocity formulas.
Horizontal And Vertical Velocity Of A Projectile
Projectile Motion Engineersfield
Projectile Motion Kinematics Homework Helpers Physics
Https Www Livephysics Com Problems And Answers Classical Mechanics Projectile Motion Pool Ball Leaves Table Initial Horizontal Velocity
The Path Of A Baseball Math Central
Projectiles Calculations Calculating The Components Of A Vector Using Trigonometry And Vertical And Horizontal Problems Ppt Download





0 comments:
Post a Comment